Unravel Sensitive Data Protection Snowflake
Overview
Most Snowflake usage data that Unravel processes is operational metadata and performance metrics, not directly identifiable personal data. Personally identifiable information (PII) can appear in SQL query text and related history tables that you must protect before sharing with Unravel. Unravel Sensitive Data Protection for Snowflake masks literals and other sensitive elements in query text while keeping structure and performance characteristics intact.
This page shows how to deploy and run Unravel Sensitive Data Protection for Snowflake using a Python stored procedure and scheduled tasks. You use Snowflake stages, stored procedures, and tasks to automate and secure data masking before Unravel reads query history.
Architecture
The sensitive data protection solution runs entirely inside your Snowflake account and sits between Snowflake system views and Unravel. Snowflake ACCOUNT_USAGE views provide query history and query text, and as the solution reads this data, it first applies Unravel Sensitive Data Protection logic from a package stored in a Snowflake stage to the QUERY_TEXT field, then writes the protected records into a dedicated output table that is shared with Unravel by using a secure share. Standard Snowflake objects—stages, procedures, tasks, and tables—orchestrate this flow, and a scheduled Snowflake task invokes the Sensitive Data Protection procedure on a CRON schedule so that the shared output table stays incrementally updated as new query history arrives.
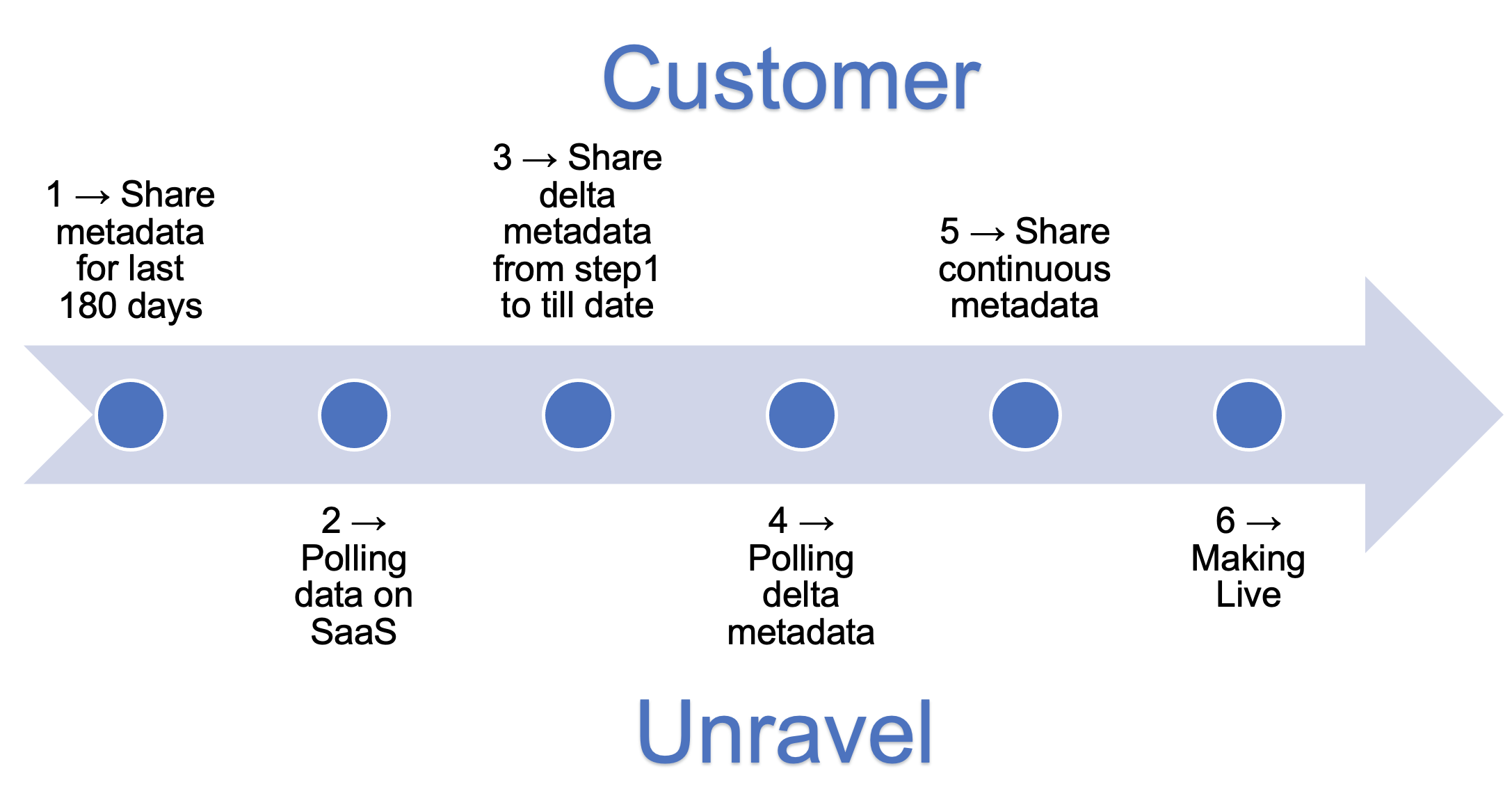
Create Snow-Share Live - Continuous Data Share with Unravel Sensitive Data Protection
Use the Snow-Share Live option to set up continuous, secure data sharing between your Snowflake environment and Unravel.
To configure the snow-share live option:
Run these steps to enable continuous secure data sharing from Snowflake to Unravel with Unravel Sensitive Data Protection.
Run step 1a from this script to create the Snowflake database, schema, stored procedures, and supporting objects required for secure data sharing with Unravel.
Update the REPLICATE_HISTORY_QUERY procedure
--PROCEDURE FOR REPLICATE HISTORY QUERY CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE REPLICATE_HISTORY_QUERY(DBNAME STRING, SCHEMANAME STRING, LOOK_BACK_DAYS STRING) returns VARCHAR(25200) LANGUAGE javascript EXECUTE AS CALLER AS $$ var taskDetails = "history_query_task ---> Getting history query data "; var task= "history_query_task"; function logError(err, taskName) { var fail_sql = "INSERT INTO REPLICATION_LOG VALUES (to_timestamp_tz(current_timestamp),'FAILED', "+"'"+ err +"'"+", "+"'"+ taskName +"'"+");" ; sql_command1 = snowflake.createStatement({sqlText: fail_sql} ); sql_command1.execute(); } function insertToReplicationLog(status, message, taskName) { var query_profile_status = "INSERT INTO REPLICATION_LOG VALUES (to_timestamp_tz(current_timestamp), "+"'"+status +"'"+", "+"'"+ message +"'"+", "+"'"+ taskName +"'"+");" ; sql_command1 = snowflake.createStatement({sqlText: query_profile_status} ); sql_command1.execute(); } var schemaName = SCHEMANAME; var dbName = DBNAME; var lookBackDays = -parseInt(LOOK_BACK_DAYS); var error = ""; var returnVal = "SUCCESS"; function truncateTable(tableName) { try { var truncateQuery = "TRUNCATE TABLE IF EXISTS "+ dbName + "." + schemaName + "." +tableName +" ;"; var stmt = snowflake.createStatement({sqlText:truncateQuery}); stmt.execute(); } catch (err) { logError(err, taskDetails) error += "Failed: " + err; } } function getColumns(tableName) { var columns = ""; var columnQuery = "SELECT LISTAGG(column_name, ', ') WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY ordinal_position) as ALL_COLUMNS FROM "+ DBNAME + ".INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS WHERE TABLE_NAME = "+"'"+tableName+"'"+" AND TABLE_SCHEMA = "+"'"+SCHEMANAME+"'"+ ";"; var stmt = snowflake.createStatement({sqlText:columnQuery}); try { var res = stmt.execute(); res.next(); columns = res.getColumnValue(1) } catch (err) { logError(err, taskDetails) error += "Failed: " + err; } return columns; } function insertToTable(tableName, isDate, dateCol, columns) { try { var insertQuery = ""; if (isDate) { insertQuery = "INSERT INTO " + dbName + "." + schemaName + "." +tableName+ " SELECT "+columns +" FROM SNOWFLAKE.ACCOUNT_USAGE."+ tableName +" WHERE "+ dateCol +" > dateadd(day, "+ lookBackDays +", current_date);"; } else { insertQuery = "INSERT INTO " + dbName + "." + schemaName + "." +tableName+ " SELECT "+columns +" FROM SNOWFLAKE.ACCOUNT_USAGE."+ tableName +";"; } var insertStmt = snowflake.createStatement({sqlText:insertQuery}); var res = insertStmt.execute(); } catch (err) { logError(err, taskDetails) error += "Failed: " + err; } } function replicateData(tableName, isDate, dateCol){truncateTable(tableName); var columns = getColumns(tableName); columns = columns.split(',').map(item => `"${item.trim()}"`).join(','); insertToTable(tableName, isDate, dateCol, columns ) return true; } insertToReplicationLog("started", "history_query_task started", task); replicateData("SESSIONS", true, "CREATED_ON"); replicateData("ACCESS_HISTORY", true, "QUERY_START_TIME"); replicateData("QUERY_INSIGHTS", true, "START_TIME"); if(error.length > 0 ) { return error; } insertToReplicationLog("completed", "history_query_task completed", task); return returnVal; $$;Create a stage for the Unravel SDP package
Create a Snowflake stage to store the Unravel Sensitive Data Protection package and grant appropriate access.
CREATE OR REPLACE STAGE DATA_MASKING_STAGE; GRANT READ ON STAGE DATA_MASKING_STAGE TO ROLE ACCOUNTADMIN; GRANT WRITE ON STAGE DATA_MASKING_STAGE TO ROLE ACCOUNTADMIN;
Verify the MD5 checksum of the unravel_sdp package, then upload the Unravel SDP package to the DATA_MASKING_STAGE.
md5sum unravel_sdp.pyc dde90e158618d25af6cd0e1c33a513dd unravel_sdp.pyc
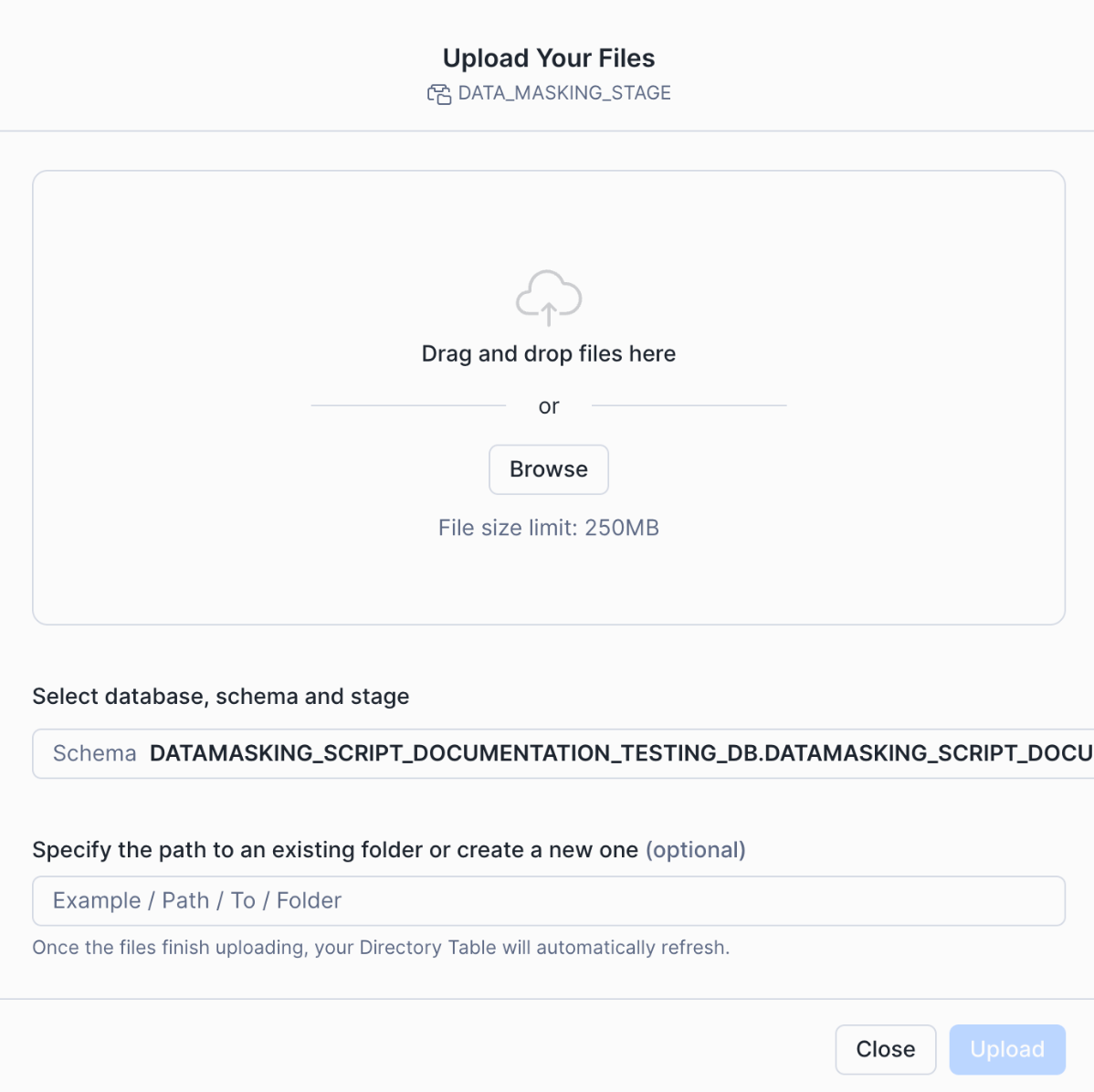
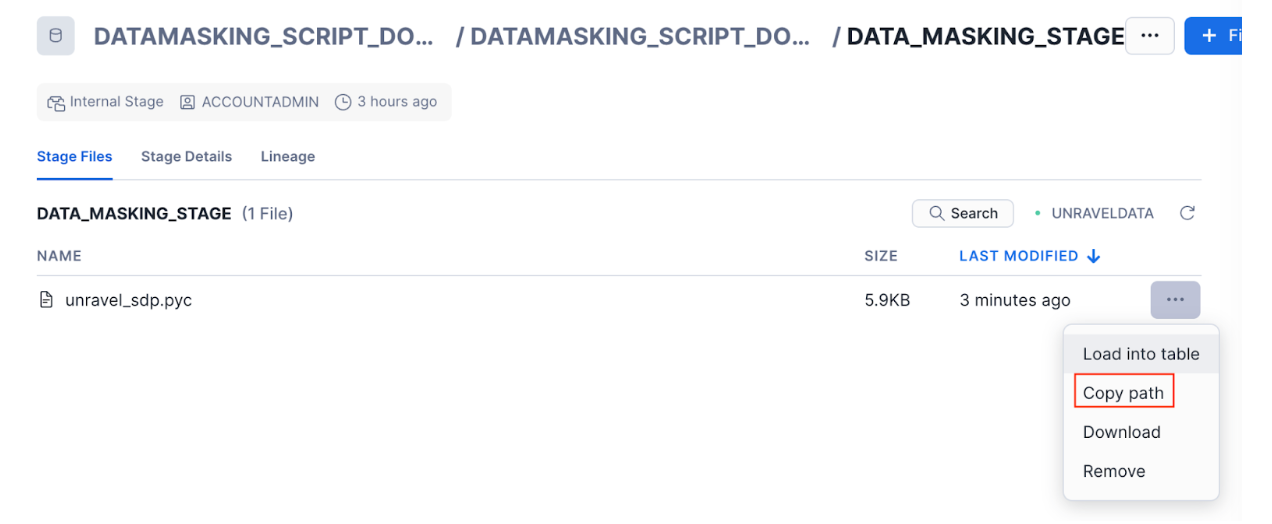
upload unravel_sdp.pyc to DATA_MASKING_STAGE by using your preferred Snowflake client or the Snowflake UI.
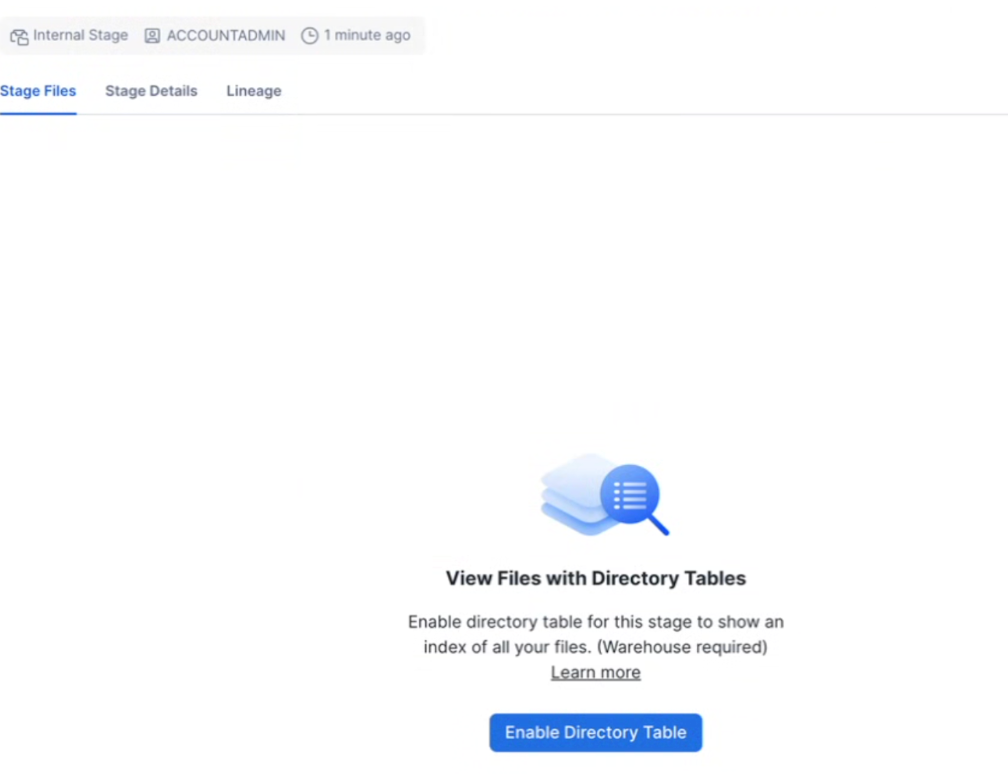
In the Snowflake UI, select Enable directory table on the stage after the upload completes successfully.
Create the sensitive data protection stored procedure
Review the parameters before you create the procedure.
look_back_days: Number of past days of data to process in each run.
source table: Fully qualified table name that contains the original query text.
destination table: Fully qualified table name where protected results are stored and shared with Unravel.
Update the IMPORTS path with the location of the uploaded unravel_sdp.pyc file in DATA_MASKING_STAGE.
Follow these steps to create the Unravel Sensitive Data Protection procedure.
This procedure reads new query history rows, applies sensitive data protection to query text, and appends protected rows to the output table.
Run the following procedures one time to perform the 180‑day data sharing load and initialize metadata for Unravel.
CALL CREATE_TABLES('UNRAVEL_SHARE','SCHEMA_4827_T'); CALL REPLICATE_ACCOUNT_USAGE('UNRAVEL_SHARE','SCHEMA_4827_T',180); CALL REPLICATE_HISTORY_QUERY('UNRAVEL_SHARE','SCHEMA_4827_T',180); CALL WAREHOUSE_PROC('UNRAVEL_SHARE','SCHEMA_4827_T'); CALL CREATE_QUERY_PROFILE('UNRAVEL_SHARE', 'SCHEMA_4827_T', '1', '14'); CALL create_shared_db_metadata('UNRAVEL_SHARE','SCHEMA_4827_T'); CALL unravel_sdp_procedure(180, 'SNOWFLAKE.ACCOUNT_USAGE.QUERY_HISTORY', 'UNRAVEL_SHARE.SCHEMA_4827_T.QUERY_HISTORY');Run the following procedure to share the replicated tables with the target Unravel Snowflake account ID.
CALL SHARE_TO_ACCOUNT('<Unravel Account Identifier>');
After the 180‑day data‑sharing load is complete, communicate the details to Unravel so Unravel can configure and start polling data.
Share delta metadata from Step 1 to current date.
Calculate the delta days using the dates when you ran Step 1 and when you plan to run Step 3:
delta days = (Step 3 date − Step 1 date) + 1
For example, if Step 1 ran on 02‑Jan and Step 3 runs on 04‑Jan, delta days = (4 − 2) + 1 = 3. Use that delta days value in the following procedure calls (replace 3 in this example with your calculated value).
CALL REPLICATE_ACCOUNT_USAGE('UNRAVEL_SHARE','SCHEMA_4827_T', 3); CALL REPLICATE_HISTORY_QUERY('UNRAVEL_SHARE','SCHEMA_4827_T', 3); CALL WAREHOUSE_PROC('UNRAVEL_SHARE','SCHEMA_4827_T'); CALL CREATE_QUERY_PROFILE('UNRAVEL_SHARE', 'SCHEMA_4827_T', '1', '3'); CALL create_shared_db_metadata('UNRAVEL_SHARE','SCHEMA_4827_T'); CALL unravel_sdp_procedure(3, 'SNOWFLAKE.ACCOUNT_USAGE.QUERY_HISTORY', 'UNRAVEL_SHARE.SCHEMA_4827_T.QUERY_HISTORY');After the delta data sharing in Step 3, communicate to Unravel. Unravel will initiate delta data loading.
Run the following statements to create and resume Snowflake tasks for continuous sharing, using schedules that meet your requirements.
CREATE OR REPLACE TASK replicate_metadata WAREHOUSE = UNRAVELDATA SCHEDULE = 'USING CRON 0 3,9,15,21 * * * UTC' AS CALL REPLICATE_ACCOUNT_USAGE('UNRAVEL_SHARE','SCHEMA_4827_T',2); CREATE OR REPLACE TASK replicate_history_query WAREHOUSE = UNRAVELDATA SCHEDULE = '60 MINUTE' AS CALL REPLICATE_HISTORY_QUERY('UNRAVEL_SHARE','SCHEMA_4827_T',2); CREATE OR REPLACE TASK createProfileTable WAREHOUSE = UNRAVELDATA SCHEDULE = '60 MINUTE' AS CALL create_query_profile('UNRAVEL_SHARE', 'SCHEMA_4827_T', '1', '2'); CREATE OR REPLACE TASK replicate_warehouse_and_realtime_query WAREHOUSE = UNRAVELDATA SCHEDULE = '720 MINUTE' AS BEGIN CALL warehouse_proc('UNRAVEL_SHARE','SCHEMA_4827_T'); END; CREATE OR REPLACE TASK shared_db_metadata_task WAREHOUSE = UNRAVELDATA SCHEDULE = '720 MINUTE' AS BEGIN CALL create_shared_db_metadata('UNRAVEL_SHARE','SCHEMA_4827_T'); END; CREATE OR REPLACE TASK unravel_sdp_procedure_task WAREHOUSE = UNRAVELDATA SCHEDULE = '60 MINUTE' AS BEGIN CALL unravel_sdp_procedure( 1, 'SNOWFLAKE.ACCOUNT_USAGE.QUERY_HISTORY', 'UNRAVEL_SHARE.SCHEMA_4827_T.QUERY_HISTORY' ); END; /** (Resume all TASKS) **/ ALTER TASK replicate_metadata RESUME; ALTER TASK replicate_history_query RESUME; ALTER TASK createProfileTable RESUME; ALTER TASK replicate_warehouse_and_realtime_query RESUME; ALTER TASK shared_db_metadata_task RESUME; ALTER TASK unravel_sdp_procedure_task RESUME;When continuous data sharing is stable and validated, communicate to Unravel. Unravel will make the SaaS account live.