AutoActions (GCP - BigQuery, Dataproc)
AutoActions automate the monitoring of your BigQuery jobs / YARN apps by allowing you to define complex, actionable policies for different cluster metrics.
Alerts can be generated by setting AutoActions. For example, you can use an AutoAction to:
Notify you about a situation that requires manual intervention, such as resource contention or stuck jobs.
The Unravel server collects various metrics from clusters, which are aggregated based on the defined AutoAction policies and scope. Violations are detected based on the trigger conditions, and accordingly, set actions are executed.
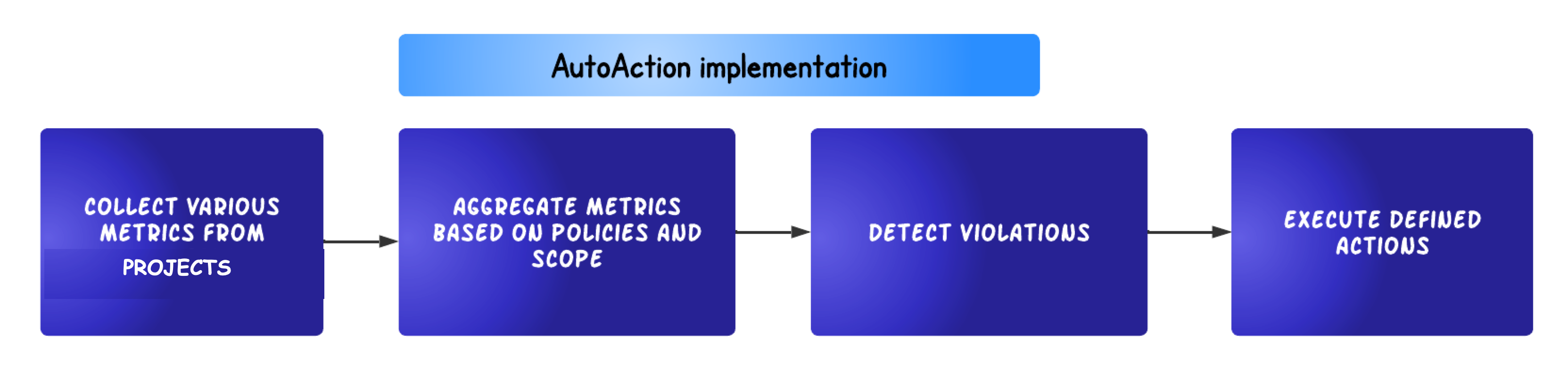
Each AutoAction policy consists of the following:
Trigger Conditions are the settings that determine when an AutoAction is violated, for example, apps using more than 2 GB of memory.
Scope Define refinements to various scopes. For example, the app is owned by User X and on cluster Y.
Actions Define the automated actions when user-defined trigger conditions are met. For example, email User X when the trigger conditions are met.
Creating AutoActions
On the Unravel UI, click the AutoActions tab.
On the AutoActions page, in the upper-right corner, click
 .
.On the New AutoAction window, select any of the following templates:
Tip
Templates are policies that you define to trigger an alert.
On the New AutoAction page, specify the following details:
Item
Description
Policy Name
Specify a policy name that reflects the purpose of the AutoAction policy.
Description
(Optional)
Describe the policy.
Active
Select the checkbox to activate the policy after you create a new AutoAction. It is not mandatory to activate a policy during creation.
Trigger Conditions
Specify the conditions when an alert should be triggered.
Metrics
Selected one of the cluster metrics. Refer to Supported cluster metrics.
Operator: Use the operator (>=) to define the threshold level of the selected metrics compared to the value.
Value: Specify the threshold value in numeric. The default value is 0 is considered if you leave the Value field empty.
Refine Scope
Click the down arrow
 and select a scope to trigger the AutoAction policy. You can refine the scope based on the following fields:
and select a scope to trigger the AutoAction policy. You can refine the scope based on the following fields: Note
Based on the selected platform, the fields displayed for the Refine Scope are changed.
Actions
Click the down arrow
 and select the action to be taken when the conditions defined in the AutoAction policy are met, and an AutoAction is triggered. You can choose from any or all of the following actions:
and select the action to be taken when the conditions defined in the AutoAction policy are met, and an AutoAction is triggered. You can choose from any or all of the following actions: Email
Enter the email ID of at least one recipient. Click Add Email to add more recipients.
Select the Include Owner checkbox to include the app's owner as a recipient of the email. The owner ID of an app can be a username (for example, John) or an email address (for example, john@acme.com).
Note
If the owner ID of an app is a username, then you must configure the base DNS for sending an email to the owner.
You can configure the base DNS using the com.unraveldata.report.user.email.domain property. For configuring email alerts and specifying email properties, see Email alerts
HTTP Post
Enter at least one URL. For example, http://localhost:8000/?notify=xyz@unraveldata.com&notify_owners=false
Ensure to open the corresponding port.
You can add more URLs by clicking Add URL.
Post to Slack
Unravel provides integration with SlackApp, which lets you post information to one more Slack channel and user. Specify the following:
Webhook URL: The incoming webhook URL configured in Slack for the channel or user. You can post to multiple webhooks.
Token: The OAuth access token for the SlackApp.
See Slack's Incoming Webhooks for more information.
Click Create.
Also, refer to the Templates section for more information.
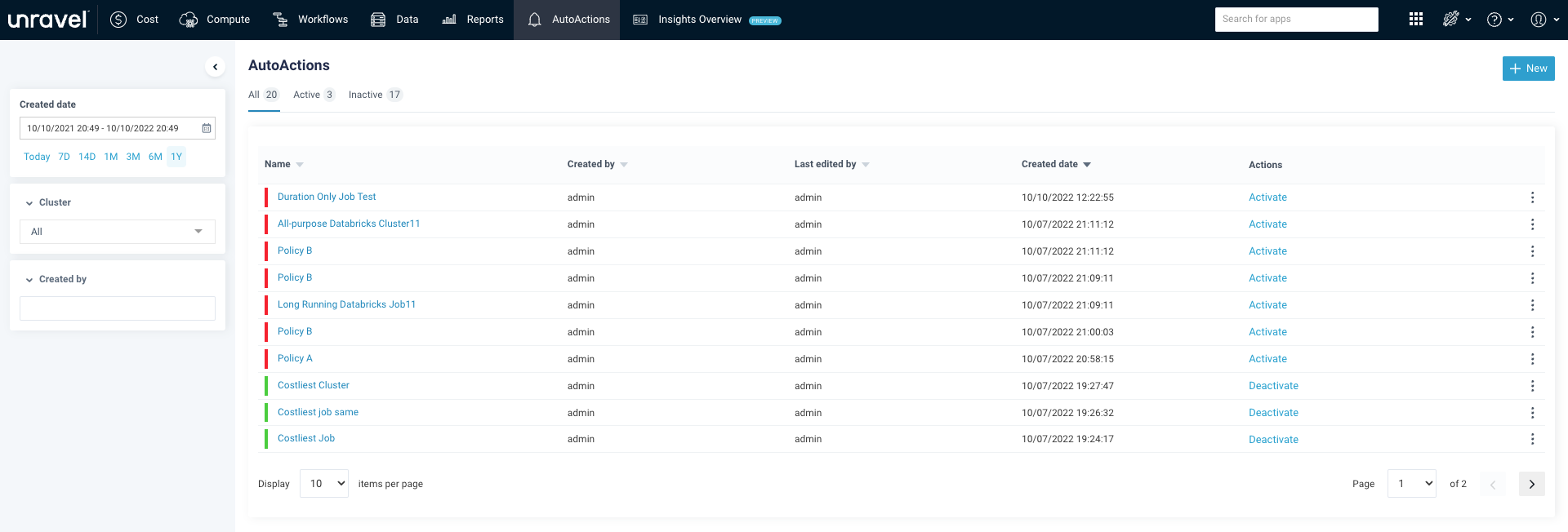
Viewing AutoActions
You can view all the AutoActions created from the AutoActions tab. To filter and view the AutoActions, do the following:
On the Unravel UI, click the AutoActions tab.
From the following, select an option to filter the AutoActions:
Created Date
Cluster
Created By
The AutoActions are listed in the following tabs:
All, where all the created AutoActions, irrespective of whether they are active or inactive, are listed. A green
 bar adjacent to an AutoAction indicates that it is active. A red
bar adjacent to an AutoAction indicates that it is active. A red  bar adjacent to an AutoAction indicates that it is inactive.
bar adjacent to an AutoAction indicates that it is inactive.Active, where only the active AutoActions are listed.
Inactive, where only the inactive Autoactions are listed.
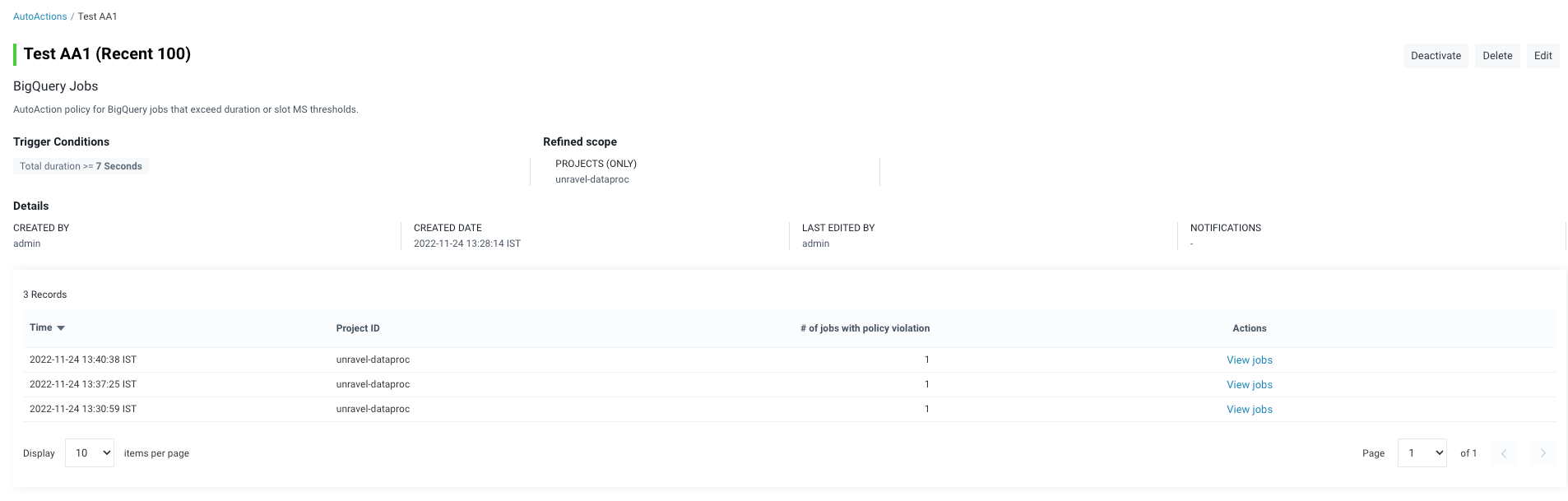
Click the name link of the AutoAction to view the history of runs and the details of the applications that violated the policy.
Click the
 icon corresponding to the AutoAction you want to edit or delete. Select Edit to edit the AutoAction details and Delete to delete the AutoAction.
icon corresponding to the AutoAction you want to edit or delete. Select Edit to edit the AutoAction details and Delete to delete the AutoAction.Click the corresponding Deactivate/Activate link to activate or inactivate an AutoAction.
Also, refer to the Limitations section to view the limitations of the AutoActions feature.
Activating or Deactivating an AutoAction
On the Unravel UI, click the AutoActions tab.
From the left panels, select an option to filter the AutoActions:
Created Date: Select a date range to view the list of AutoActions. You can either specify a custom range or choose one of the date range options (Today, 7 days, 14 days, 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, 1 year)
Cluster: Select a cluster to view the AutoActions created for that specific cluster. You can only choose a single cluster at a time.
Created By: Type a user's name to view the list of AutoActions created by that user.
The AutoActions are listed in the following tabs:
All, where all the created AutoActions, irrespective of whether they are active or inactive, are listed.
Active, where only the active AutoActions are listed.
Inactive, where only the inactive AutoActions are listed.
Do any of the following to activate or deactivate an AutoAction.
In the AutoAction tabs > AutoAction list, click the Deactivate/Activate link corresponding to an AutoAction.
On the AutoAction tabs > AutoAction list, click the AutoAction link. The corresponding AutoAction details page is displayed. Click the Deactivate/Activate tab.
Editing an AutoAction
On the Unravel UI, click the AutoActions tab.
From the following, select an option to filter the AutoActions:
Created Date
Cluster
Created By
The AutoActions are listed in the following tabs:
All, where all the created AutoActions, irrespective of whether they are active or inactive, are listed.
Active, where only the active AutoActions are listed.
Inactive, where only the inactive Autoactions are listed.
In the Actions column, click the
 icon corresponding to the AutoAction you want to edit.
icon corresponding to the AutoAction you want to edit. Select Edit to edit the AutoAction details.
Deleting an AutoAction
On the Unravel UI, click the AutoActions tab.
From the following, select an option to filter the AutoActions:
Created Date
Cluster
Created By
The AutoActions are listed in the following tabs:
All, where all the created AutoActions, irrespective of whether they are active or inactive, are listed.
Active, where only the active AutoActions are listed.
Inactive, where only the inactive AutoActions are listed.
In the Actions column, click the
 icon corresponding to the AutoAction you want to delete.
icon corresponding to the AutoAction you want to delete. Select Delete to delete the AutoAction details.
Regular Expressions (regex)
You can add regular expressions (regex) to AutoActions templates when you narrow the scope of User and Project with Only or Except. You must first select the scope (User, Project, Time ) and only specify the regular expressions in the Transform box. Ensure always to select a scope before you specify the regex.
In the following example, regex is used to define the user scope.
{"enabled":true,"admin":true,"policy_name":"BigQuery Job","policy_id":1121,"instance_id":"6252699361701385875","name_by_user":"Long running BigQuery Job","description_by_user":"AutoAction policy for BigQuery jobs that exceed duration or slot MS thresholds.","created_by":"admin","last_edited_by":"admin","created_at":1667411797141,"updated_at":1667411797141,"entity_type":"bigquery","rules":[{"scope":"bigqueryjobs","metric":"bigqueryDuration","compare":">=","value":1}],"actions":[],"cluster_mode":0,"cluster_list":[],"cluster_transform":"","queue_mode":0,"queue_list":[],"queue_transform":"","user_mode":2,"user_list":["vlad","sandip"],"user_transform":"regex/^.*[.](.+)[.](.+)$/$2/","app_mode":1,"app_list":[],"app_transform":"","sustain_mode":0,"sustain_time":0,"time_mode":0}Note
Keyword regex is mandatory. regex keyword is similar to substitute s in regular expressions.