AutoActions
AutoActions automate the monitoring of your YARN apps and Impala queries by allowing you to define complex, actionable rules on different cluster metrics.
For example, you can use an AutoAction to:
Apps: Notify you about a situation that requires manual intervention, such as resource contention or stuck jobs.
Impala: Monitor Impala jobs based on long-running Impala queries and rogue Impala applications (HDFS Read/Write). For example, DevOps wants to receive alerts on Impala refresh jobs.
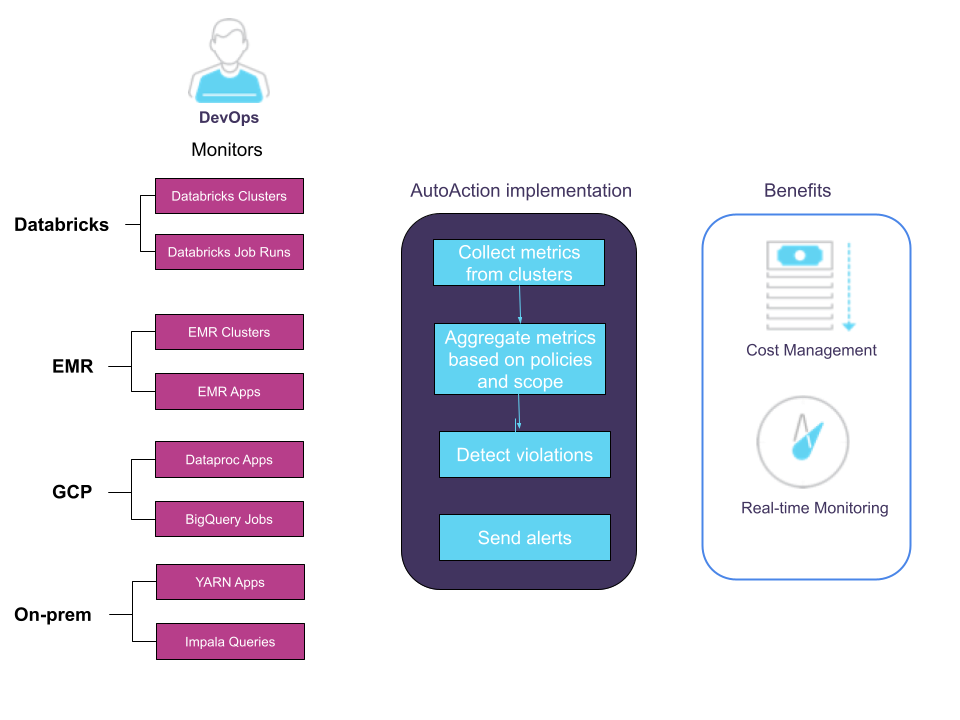
Consider a scenario where the DevOps monitors clusters. The Unravel server processes AutoActions by:
Collecting various metrics from the cluster
Aggregating the metrics according to user-defined triggers (rule) and scope
Detecting violations
Executing the defined actions for each rule violation. Each rule consists of the:
Trigger Conditions are the settings that determine when an AutoAction is violated.
For example, apps using more than 2 GB of memory.
Scope Define refinements to various scopes.
For example, the app is owned by User X on Cluster Y.
Actions Define the automated actions when user-defined trigger conditions are met. For example, email User X when the trigger conditions are met.
DevOps can quickly take action to control costs by terminating the cluster if necessary. Using Unravel to detect and send alerts allows for real-time monitoring and cost management.