Part 1: Installing Unravel on a separate Azure VM
This topic explains how to install Unravel on an Azure VM with required network setup to connect the Unravel VM to your Azure Databricks workspaces.
Important
If you have not already done so, confirm your new node meets Unravel's hosting requirements.
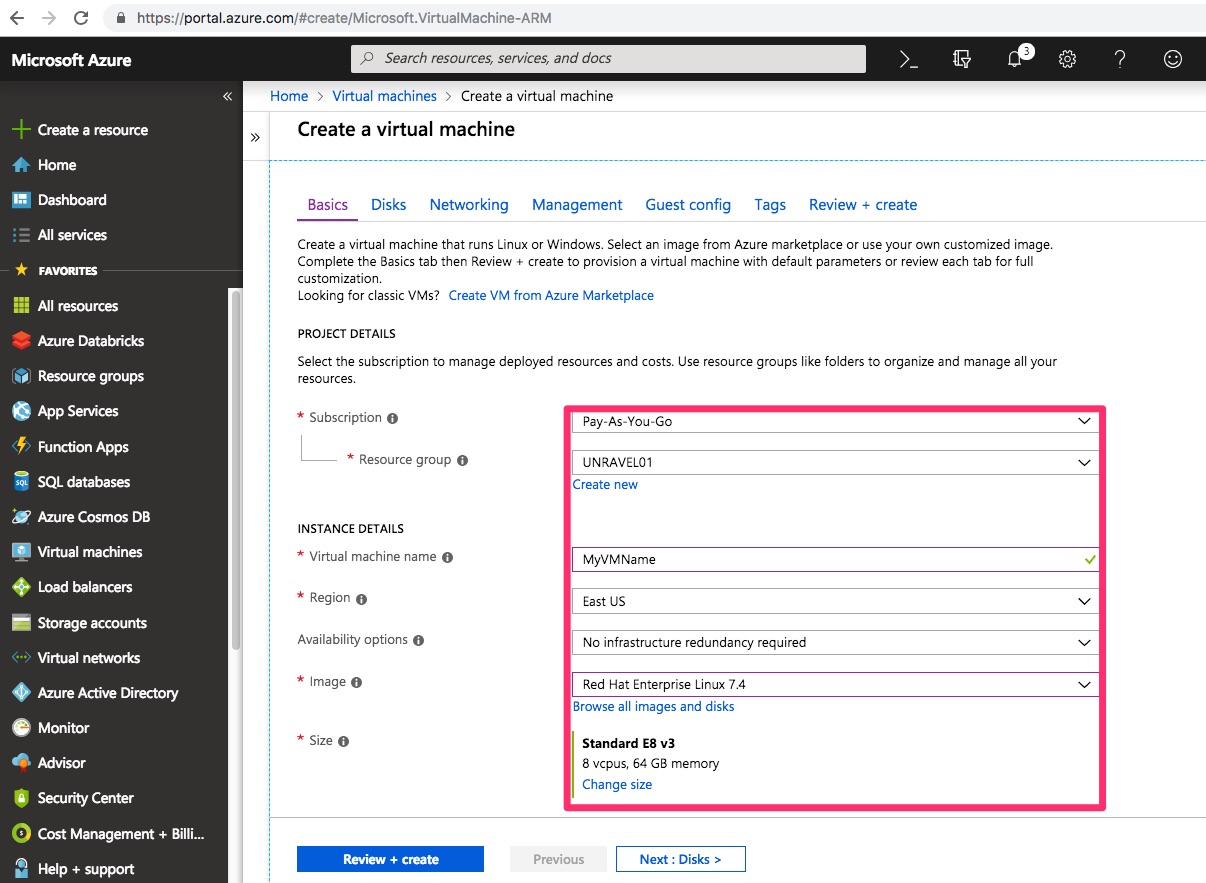
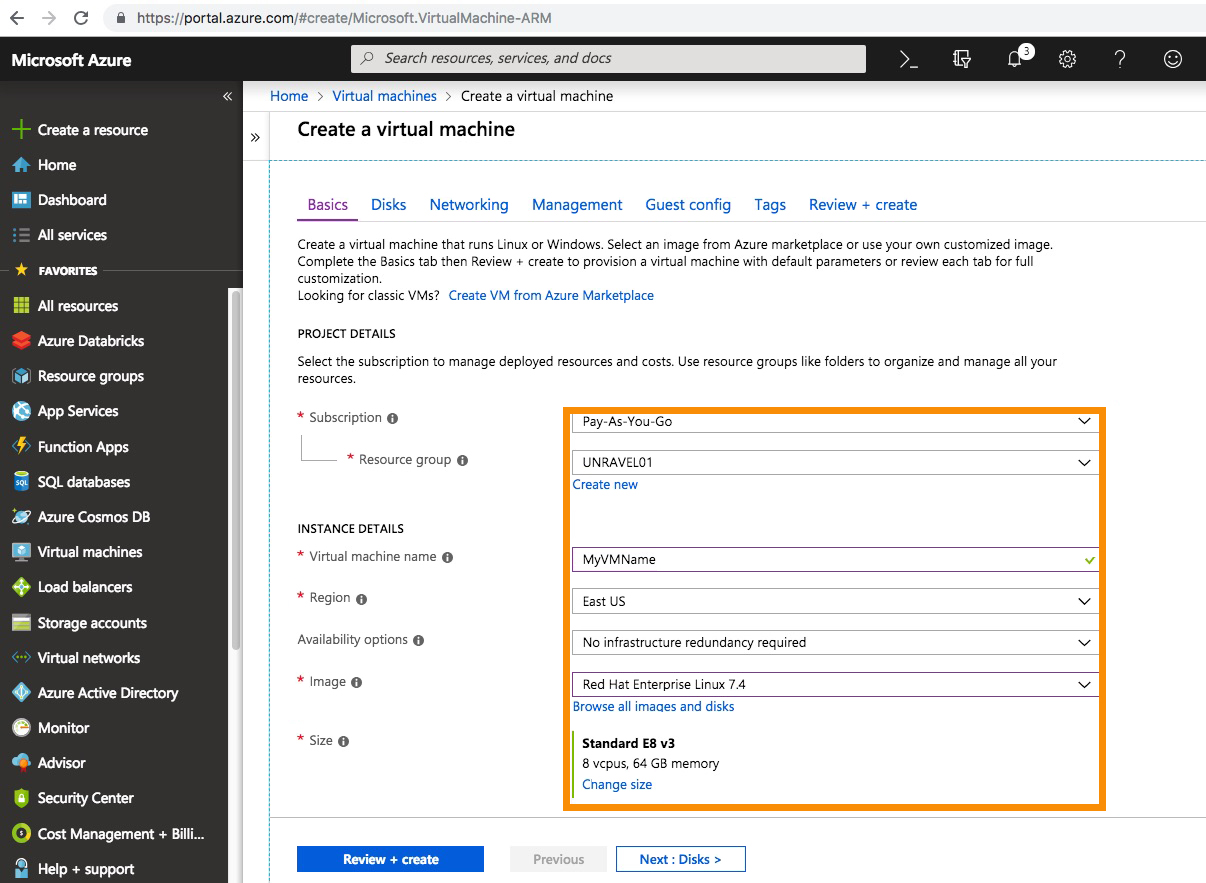
1. Provision an Azure VM for Unravel Server
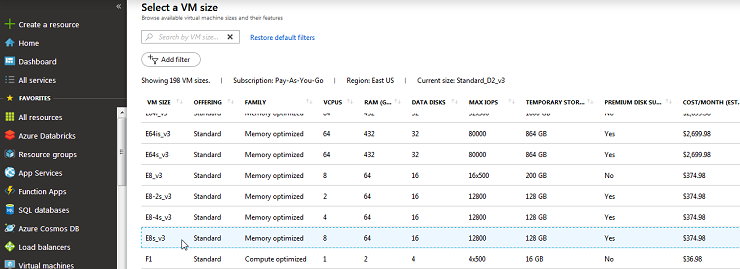
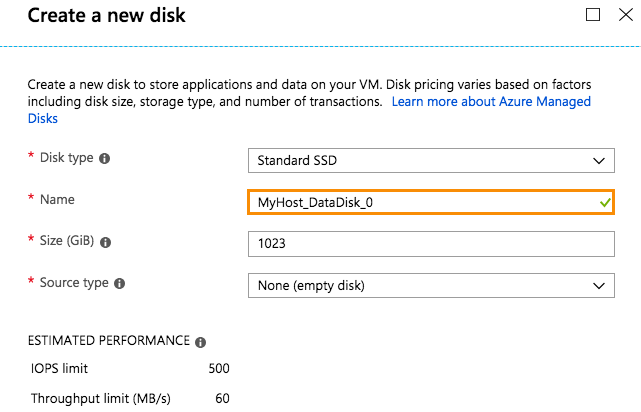
2. Configure the VM
4. Install Unravel Server on the VM
6. Configure Unravel Server with basic options
Open an SSH session to the Unravel VM.
ssh -i
ssh-private-keyssh-user@unravel-hostSet correct permissions on the Unravel configuration directory.
cd /usr/local/unravel/etc sudo chown unravel:unravel *.properties sudo chmod 644 *.properties
In
/usr/local/unravel/etc/unravel.properties, add/modify the following properties:Set general properties:
com.unraveldata.onprem=false com.unraveldata.cluster.type=DB com.unraveldata.python.enabled=false com.unraveldata.tagging.enabled=true
Optionally modify the following properties:
com.unraveldata.spark.appLoading.delayForRetry=60000 com.unraveldata.databricks.http.conn.timeout=5 com.unraveldata.databricks.http.read.timeout=10
Allow network access to the Unravel VM from Databricks workspaces:
Assign public IP and add firewall rules to open the required ports as follows.
Databricks cluster nodes are created in their own virtual network "workers-vnet". And for these cluster nodes access to Unravel VM’s secured service endpoint, you need to open Unravel VM’s secured service endpoints to the public. This means Unravel secure services ports (3000, 4043, and 4443) need to be opened to the public on Unravel VM’s virtual network and then mapped to Unravel VM, by following the steps below.
Log into the Azure portal.
Click Virtual Machines service and select the Unravel VM.
Click Networking.
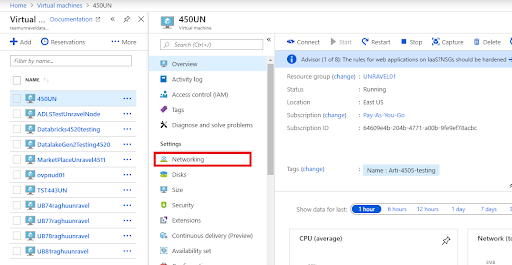
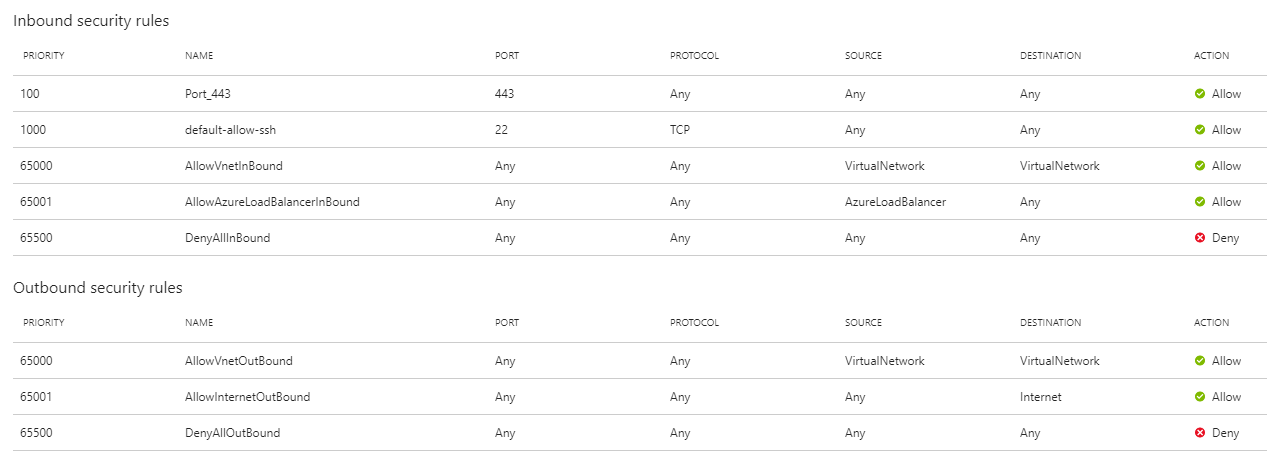
The networking settings of the Unravel VM are displayed. The settings include the virtual network, subnet, and security group which the VM is currently using.
Click Inbound port rule.
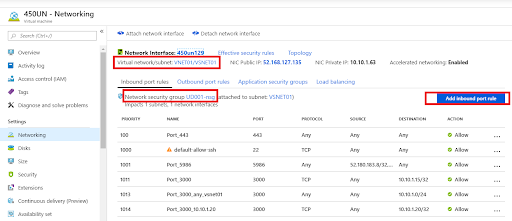
Add an inbound rule to the network security group to allow port 3000, 4043 and 4443 on the internal IP address of the Unravel VM.
In the screenshot below, the internal IP address of the Unravel VM is
10.10.1.63.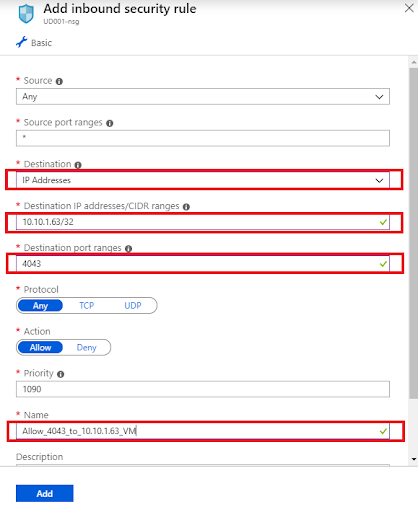
You should now see the following three inbound rules added to the network security group:
Rule name
Port
Protocol
Source
Destination
Allow_port_3000_to_Unravel_VM
3000
Any
Any
Unravel_VM_internal_IP
Allow_port_4043_to_Unravel_VM
4043
Any
Any
Unravel_VM_internal_IP
Allow_port_4443_to_Unravel_VM
4443
Any
Any
Unravel_VM_internal_IP
Generate Databricks personal access token for all workspaces.
In the Generate New Token dialog, enter these settings:
Workspace name
Workspace ID
Databricks instance
Databricks personal access token
Tip
Unravel uses this token to authenticate and access Databricks REST API and DBFS CLI.
For information on how to generate the token, see https://docs.databricks.com/api/latest/authentication.html#generate-a-token
Unlike passwords, tokens expire and can be revoked. If a token expires, replace it with a new one and re-run
databricks_setup.sh. To identify expired tokens, check the Unravel logs (look for "authentication errors") and Unravel UI (look for missing Databricks metadata).
Install DBFS CLI on the Azure VM host.
Note
This CLI needs a Python version newer than 2.7.9.
Run
databricks_setup.shto install Unravel agents on Azure Databricks workspaces.
7. Start Unravel services
sudo /etc/init.d/unravel_all.sh restart
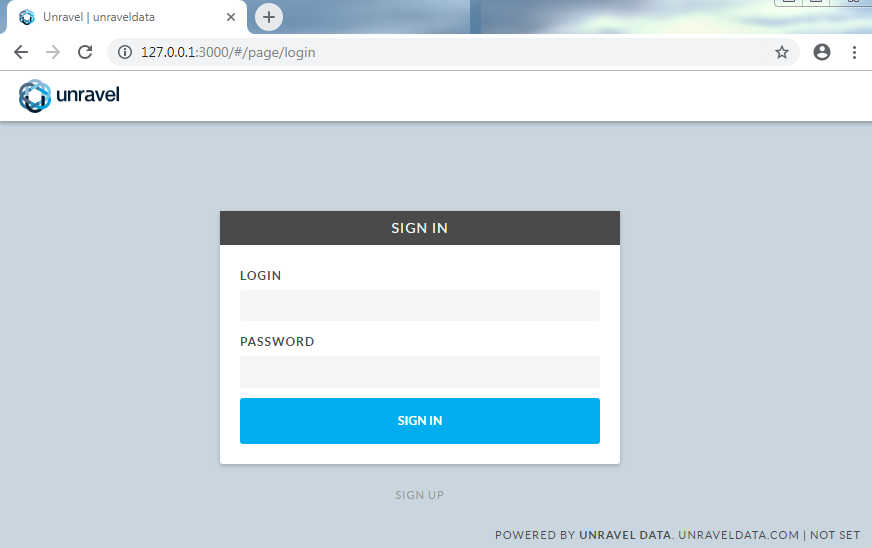
8. Log into Unravel UI
Congratulations! Unravel Server is up and running. Proceed to Part 2: Connecting Unravel to a Databricks cluster.