Amazon Web Services (AWS) Databricks
Before installing Unravel in AWS Databricks, check and ensure that the installation requirements are completed and follow the below instructions to install and configure Unravel:
1. Create an EC2 instance and connect Databricks to Unravel VM
On your AWS Console, go to the EC2 dashboard and click Launch Instance.
Select the following options based on Unravel's instance requirements:
Base OS
Instance type and size
Ports
Networking
The EC2 instance must be in the same region as the target
clusters, which Unravel EC2 node will be monitoring.
Security groups or policies
Create a security group that allows port 3000 and port 4043 from the cluster nodes' IP address, and put the security group member used on the cluster in this rule.
Sample inbound rule Type
Protocol
Port range
Source
All traffic
All
All
Security group ID of this group or subnet IP block.
For example, 10.10.0.0/16
SSH
TCP
22
0.0.0.0/0 or trusted public IP for SSH access
Custom TCP Rule
TCP
443
Security group ID used on the cluster or subnet IP block (if the IP block belongs to a different VPC). Required for VPC peering connection
Custom TCP Rule
TCP
3000
Security group ID used on the cluster or subnet IP block (if the IP block belongs to a different VPC). Required for VPC peering connection.
Custom TCP Rule
TCP
4043
Security group ID used on the cluster or subnet IP block (if the IP block belongs to a different VPC). Required for VPC peering connection.
Custom TCP Rule
TCP
4443
Security group ID used on the cluster or subnet IP block (if the IP block belongs to a different VPC). Required for VPC peering connection.
Review the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) Peering options to connect Databricks with the Unravel VM.
Workspace | VPC Peering Options |
|---|---|
Workspace and Unravel VM are in the same VPC | - |
Workspace VPC is in a different Region | Use VPC Peering: |
Workspace VPC is in a different AWS account | Use VPC Peering: |
2. Download Unravel
3. Deploy Unravel
Unravel binaries are available as a TAR file or RPM package. You can deploy the Unravel binaries in any directory on the server. However, the user who installs Unravel must have the write permissions to the directory where the Unravel binaries are deployed.
After you extract the contents of the TAR file or RPM package, unravel directory is created within the installation directory (<unravel_installation_directory>) and Unravel will be available in <Unravel_installation_directory>/unravel. The directory layout will be unravel/versions/<Directories and files>.
The following steps to deploy Unravel from a TAR file should be performed by a user, who will run Unravel.
Create an Installation directory.
mkdir
/path/to/installation/directoryFor example: mkdir /opt/
Extract Unravel tar file to the installation directory, which you have created in the first step. After you extract the contents of the TAR file,
unraveldirectory is created within the installation directory.tar zxf unravel-
<version>tar.gz -C</path/to/installation/directory>For example: tar zxf unravel-4.7.0.0.tar.gz -C /opt
The unravel directory will be available within
/opt.Grant ownership of the directory to a user who will run Unravel.
chown -R username:groupname
</path/to/installation/directory>For example: chown -R hadoop:hadoop /opt/unravel/
Important
The following steps to deploy Unravel from an RPM package should be performed by a root user. After the RPM package is deployed, the remaining installation procedures should be performed by unravel user.
Create an installation directory.
mkdir /usr/local/unravel
Run the following command:
rpm -i unravel-
<version>.rpmFor example: rpm -i unravel-4.7.0.0.rpm
The unravel directory will be available in
/usr/local.If you want to provide a different location, use the --prefix command.
For example:
mkdir /opt/unravel
rpm -i unravel-4.7.0.0.rpm --prefix /opt
The unravel directory will be available in
/opt.Grant ownership of the directory to a user who will run Unravel. This user executes all the processes involved in Unravel installation.
chown -R
username:groupname/usr/local/unravelFor example: chown -R hadoop:hadoop /usr/local/unravel
Continue with the installation procedures as unravel user.
4. Install Unravel
You can install Unravel either with Interactive Precheck or manually without Interactive Precheck.
Note
Unravel recommends installation with Interactive Precheck.
To install Unravel with Interactive precheck, you must run the Interactive Precheck utility to generate a bootstrap configuration file for installation.
5. Configure Unravel Log Receiver
Stop Unravel.
<unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/manager stopReview and update Unravel Log Receiver (LR) endpoint. By default, this is set to local FQDN only visible to workspaces within the same network. If this is not the case, run the following to set the LR endpoint:
<unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/manager config databricks set-lr-endpoint<hostname>''For example: /opt/unravel/manager config databricks set-lr-endpoint <hostname> ''
After you run this command, you are prompted to specify the port number. Ensure to press ENTER and leave it empty.
Apply the changes.
<Unravel installation directory>/unravel/manager config apply<Unravel installation directory>/unravel/manager refresh databricksStart all the services.
<unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/manager start
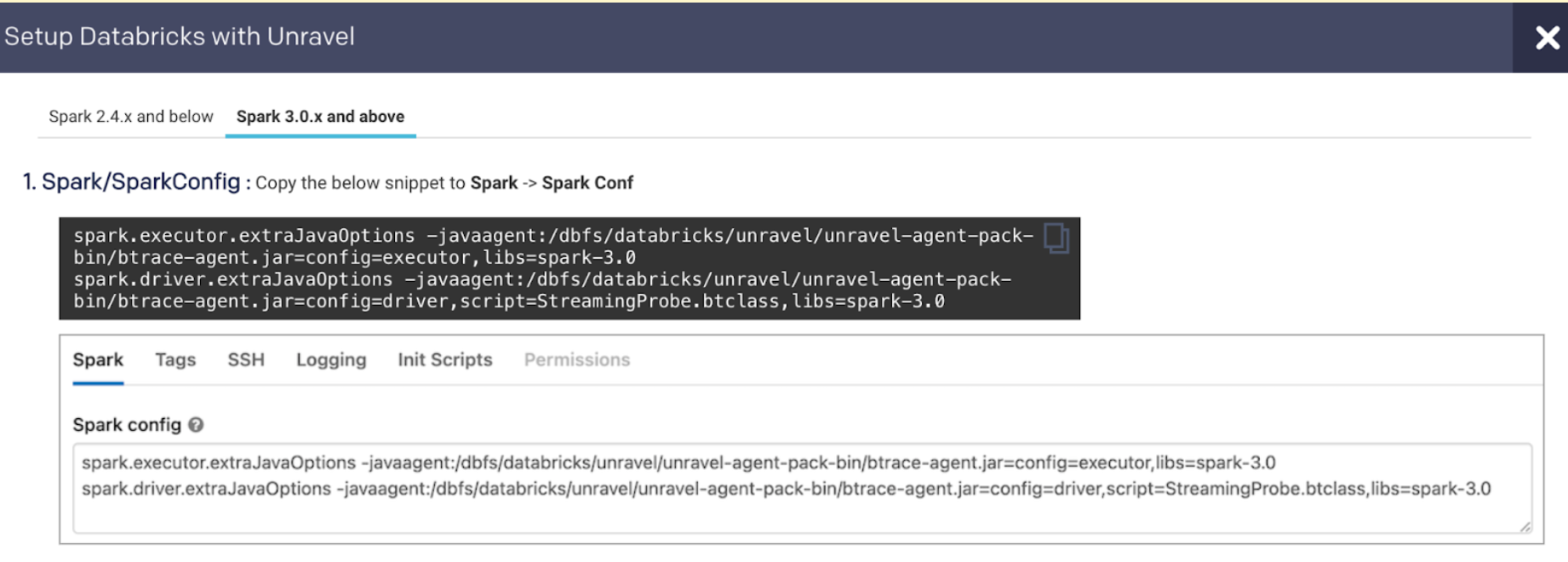
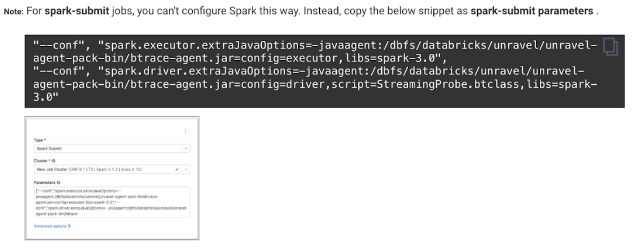
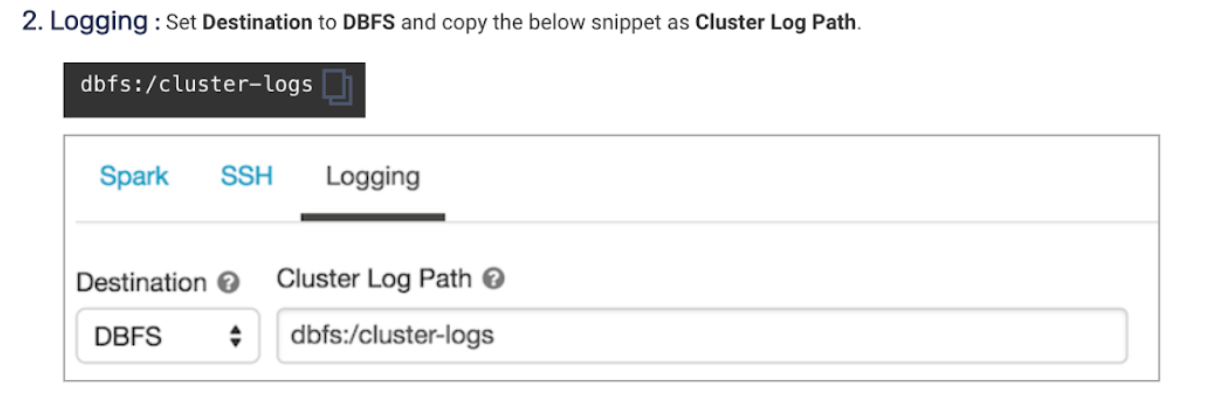
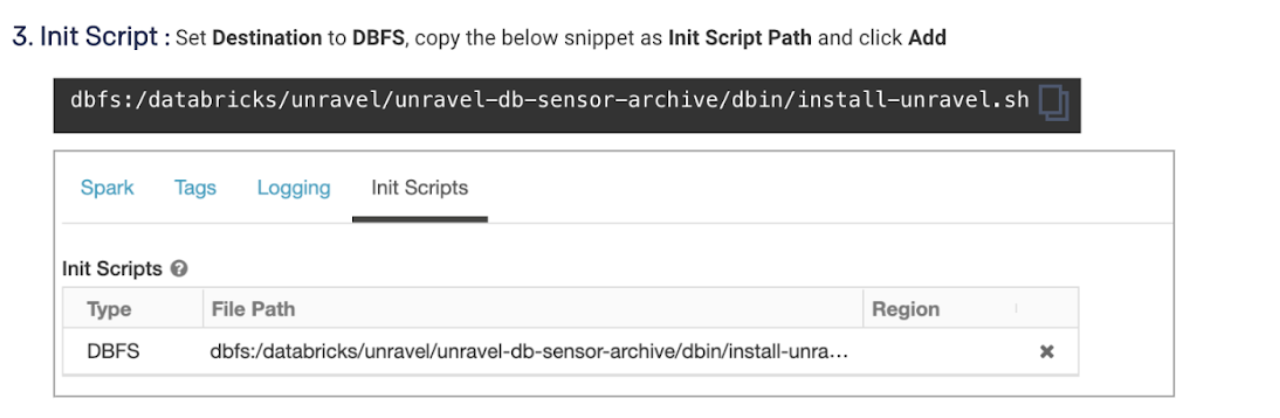
6. Connect Databricks cluster to Unravel
Run the following steps to connect the Databricks cluster to Unravel.