Microsoft Azure Databricks
Before installing Unravel in Azure Databricks, check and ensure that the Unravel installation requirements are completed and follow the below instructions to install and configure Unravel:
1. Create Unravel VM, create Azure Databricks, and install Unravel Prerequisites on Azure VM
5. Connect Databricks cluster to Unravel
1. Create Unravel VM, create Databricks, and install DBFS CLI
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Select Virtual Machines > Add and enter the following information in the Basics tab:
Project Details
Subscription
Choose the applicable subscription.
Resource group
Create a new group or choose an existing one.
Instance Details
Virtual Machine Name:
The Unravel server name.
Region:
Select the Azure region.
Availability Options
Select
No infrastructure is redundancy required.Image
Select the appropriate image. Both
Centos-based 7.x+ andRed Hat Enterprise Linux 7.x+ are supported.Size
Click Change Size. In the modal, select Memory-optimized image with at least
128 GB memoryandPremium Disk support, for example, E16s_v3 in East US 2)Administrator account
Authentication type
Select
passwordorSSH Key.Username and Password
Enter your VM login information.
Inbound Port Rules
Public inbound ports
Select Allow selected ports.
Selected Inbound ports
Select both
HTTPSandSSH.Click Next: Disks > and enter the following information in the Disks tab.
Disk Options
OS disk type: Select
Premium SSD.
Data Disk
Click Create and attach a new disk.
Caution
This disk is formatted, so do not choose the Attach an existing disk option.
Enter a Name.
Select Source type
None (empty disk).Set Size to at least 512 GiB.
Account type: Select
premium SSD.
Click Next: Networking > and enter the following information:
Virtual network: Create a new or choose an existing one.
Subnet: Create a new or choose an existing one.
Public IP: Create a new or choose an existing one.
Select Inbound ports: Select
HTTPSandSSH.
Click Review + create. Your deployment is now created.
Select Go to Resource > Networking > Inbound port rules > Add inbound port rule and include the following ports.
Rule Name
Destination
Destination IP Address
Destination Port Ranges
Unravel_3000
IP Addresses
NIC Private IP
3000
Unravel_443
IP Addresses
NIC Private IP
443
Unravel_4043
IP Addresses
NIC Private IP
4043
Click OK.
Select Create a resource > Azure Databricks > Create. Go directly to step#3 if you already have workspaces.
Select Workspace name, Subscription, Resource group, Location, and Pricing tier.
Review VNET Peering options to connect Databricks with Unravel VM.
2. Download Unravel
3. Deploy Unravel
4. Run setup
You can run the setup command to install Unravel. The setup command allows you to do the following:
Runs Precheck automatically to detect possible issues that prevent a successful installation. Suggestions are provided to resolve issues. Refer to Precheck filters for the expected value for each filter.
Let you run extra parameters to integrate the database of your choice.
The setup command allows you to use a managed database shipped with Unravel or an external database. The setup uses the Unravel managed PostgreSQL database when run without any additional parameters. Otherwise, you can specify one of the following types of databases in the setup command:
MySQL (Unravel managed as well as external MySQL database)
MariaDB (Unravel managed as well as external MariaDB database)
PostgreSQL (External PostgreSQL)
Refer to Integrate database for details.
Let you specify a separate path for the data directory other than the default path.
You can locate the Unravel data and configurations in the
datadirectory. By default, the installer maintains the data directory under<Unravel installation directory>/data. You can also change the data directory's default location by running additional parameters with the setup command. To install Unravel with the setup command.Provides more setup options.
Notice
The Unravel user who owns the installation directory should run the setup command to install Unravel.
To install Unravel with the setup command, do the following:
Switch to Unravel user.
su -
<unravel user>Run setup command:
Note
Refer to setup Options for all the additional parameters that you can run with the setup command
Refer to Integrate database topic and complete the pre-requisites before running the setup command with any other database other than Unravel managed PostgreSQL, which is shipped with the product. Extra parameters must be passed with the setup command when using another database.
Tip
Optionally, if you want to provide a different data directory, you can pass an extra parameter (--data-directory) with the setup command as shown below:
<unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/versions/
<Unravel version>/setup --enable-databricks --data-directory/the/data/directorySimilarly, you can configure separate directories for other unravel directories —contact support for assistance.
PostgreSQL
Unravel managed PostgreSQL
<unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/versions/
<Unravel version>/setup --enable-databricksExternal PostgreSQL
<unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/versions/
<Unravel version>/setup --enable-databricks --external-database postgresql<HOST><PORT><SCHEMA><USERNAME><PASSWORD>/ ##TheHOST,PORT,SCHEMA,USERNAME,PASSWORDare optional fields and are prompted if missing. ##For example: /opt/unravel/versions/abcd.992/setup --enable-databricks --external-database postgresql xyz.unraveldata.com 5432 unravel_db_prod unravel unraveldata
MySQL
Unravel managed MySQL
<unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/versions/
<Unravel version>/setup --enable-databricks --extra /tmp/mysqlExternal MySQL
<unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/versions/
<Unravel version>/setup --enable-databricks --extra /tmp/<MySQL-directory> --external-database mysql<HOST><PORT><SCHEMA><USERNAME><PASSWORD>##TheHOST,PORT,SCHEMA,USERNAME,PASSWORDare optional fields and are prompted if missing.
MariaDB
Unravel managed MariaDB
<unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/versions/
<Unravel version>/setup --enable-databricks --extra /tmp/mariadbExternal MariaDB
<unravel_installation_directory>unravel/versions/
<Unravel version>/setup --enable-databricks --extra /tmp/<MariaDB-directory>--external-database mariadb<HOST><PORT><SCHEMA><USERNAME><PASSWORD>##TheHOST,PORT,SCHEMA,USERNAME,PASSWORDare optional fields and are prompted if missing.
Precheck is automatically run when you run the setup command. Refer to Precheck filters for the expected value for each filter.
Review and update Unravel Log Receiver (LR) endpoint. By default, this is set to local FQDN only visible to workspaces within the same network. If this is not the case, run the following to set the LR endpoint:
<unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/manager config databricks set-lr-endpoint
<hostname><port>## For example: /opt/unravel/manager config databricks set-lr-endpoint unravel.server.com 4043Apply the changes.
<Unravel installation directory>/unravel/manager config apply <Unravel installation directory>/unravel/manager refresh databricks
Start all the services.
<unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/manager start
Check the status of services.
<unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/manager report
The following service statuses are reported:
OK: Service is up and running.
Not Monitored: Service is not running. (Has stopped or has failed to start)
Initializing: Services are starting up.
Does not exist: The process unexpectedly disappeared. A restart will be attempted ten times.
You can also get the status and information for a specific service. Run the manager report command as follows:
<unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/manager report <service> ## For example: /opt/unravel/manager report auto_action
The Precheck output displays the issues that prevent a successful installation and provides suggestions to resolve them. You must resolve each of the issues before proceeding. See Precheck filters.
After resolving the precheck issues, you must re-login or reload the shell to execute the setup command again.
Note
You can skip the precheck using the setup --skip-precheck command in certain situations.
For example:
/opt/unravel/versions/<Unravel version>/setup --skip-precheck
You can also skip the checks that you know can fail. For example, if you want to skip the Check limits option and the Disk freespace option, pick the command within the parenthesis corresponding to these failed options and run the setup command as follows:
setup --filter-precheck ~check_limits,~check_freespace
Tip
Run --help with the setup command and any combination of the setup command for complete usage details.
<unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/versions/<Unravel version>/setup --help
/opt/unravel/versions/abcd.1004/setup 2021-04-05 15:51:30 Sending logs to: /tmp/unravel-setup-20210405-155130.log 2021-04-05 15:51:30 Running preinstallation check... 2021-04-05 15:51:31 Gathering information ................. Ok 2021-04-05 15:51:51 Running checks .................. Ok -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- system Check limits : PASSED Clock sync : PASSED CPU requirement : PASSED, Available cores: 8 cores Disk access : PASSED, /opt/unravel/versions/develop.1004/healthcheck/healthcheck/plugins/system is writable Disk freespace : PASSED, 229 GB of free disk space is available for precheck dir. Kerberos tools : PASSED Memory requirement : PASSED, Available memory: 79 GB Network ports : PASSED OS libraries : PASSED OS release : PASSED, OS release version: centos 7.6 OS settings : PASSED SELinux : PASSED -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Healthcheck report bundle: /tmp/healthcheck-20210405155130-xyz.unraveldata.com.tar.gz 2021-04-05 15:51:53 Prepare to install with: /opt/unravel/versions/abcd.1004/installer/installer/../installer/conf/presets/default.yaml 2021-04-05 15:51:57 Sending logs to: /opt/unravel/logs/setup.log 2021-04-05 15:51:57 Instantiating templates ................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:05 Creating parcels .................................... Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:20 Installing sensors file ............................ Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:20 Installing pgsql connector ... Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:22 Starting service monitor ... Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:27 Request start for elasticsearch_1 .... Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:27 Waiting for elasticsearch_1 for 120 sec ......... Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:35 Request start for zookeeper .... Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:35 Request start for kafka .... Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:35 Waiting for kafka for 120 sec ...... Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:37 Waiting for kafka to be alive for 120 sec ..... Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:42 Initializing pgsql ... Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:46 Request start for pgsql .... Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:46 Waiting for pgsql for 120 sec ..... Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:47 Creating database schema ................. Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:50 Generating hashes .... Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:52 Loading elasticsearch templates ............ Ok 2021-04-05 15:52:55 Creating kafka topics .................... Ok 2021-04-05 15:53:36 Creating schema objects ....................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... Ok 2021-04-05 15:54:03 Request stop ....................................................... Ok 2021-04-05 15:54:16 Done [unravel@xyz ~]$
5. Connect Databricks cluster to Unravel
Run the following steps to connect the Databricks cluster to Unravel. You can also refer to the video tutorial:
Register workspace in Unravel using one of the following options:
Option 1: From Unravel UI
Go to the Unravel Instance UI and from the upper right click
 > Workspaces. The Workspaces Manager page is displayed.
> Workspaces. The Workspaces Manager page is displayed.Click Add Workspace and enter the following details.
Field
Description
Workspace Id
Databricks workspace ID, which can be found in the Databricks URL.
Workspace Name
Databricks workspace name, which can be found in the Databricks URL.
Instance (Region) URL
Regional URL where the Databricks workspace is deployed.
Tier
Select a subscription option: Standard or Premium.
Token
Personal access token to access Databricks REST APIs. Refer to Authentication using Databricks personal access tokens to create personal access tokens.
Note
Personal access tokens can be created with admin or non-admin roles.
Note
After you click the Add button, it will take around 2-3 minutes to register the Databricks Workspace with Unravel.
Restart Unravel.
<Unravel installation directory>/unravel/manager restart
Option 2: From command-line using manager command.
Stop Unravel
<Unravel installation directory>/unravel/manager stop
Switch to Unravel user.
Add the workspace details using the manager command as follows from the Unravel installation directory:
source
<path-to-python3-virtual environment-dir>/bin/activate <Unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/manager config databricks add --id <workspace-id> --name<workspace-name>--instance<workspace-instance>--access-token<workspace-token>--tier<tier_option>##For example: /opt/unravel/manager config databricks add --id 0000000000000000 --name myworkspacename --instance https://adb-0000000000000000.16.azuredatabricks.net --access-token xxxx --tier premiumApply the changes.
<Unravel installation directory>/unravel/manager config apply
Start Unravel
<Unravel installation directory>/unravel/manager start
Add Unravel configuration to Databricks clusters. Go to Unravel UI and from the upper right click Manage
 > Workspaces > Cluster configuration to get the configuration details. Follow the instructions and update every cluster (Automated /Interactive) in your workspace.
> Workspaces > Cluster configuration to get the configuration details. Follow the instructions and update every cluster (Automated /Interactive) in your workspace.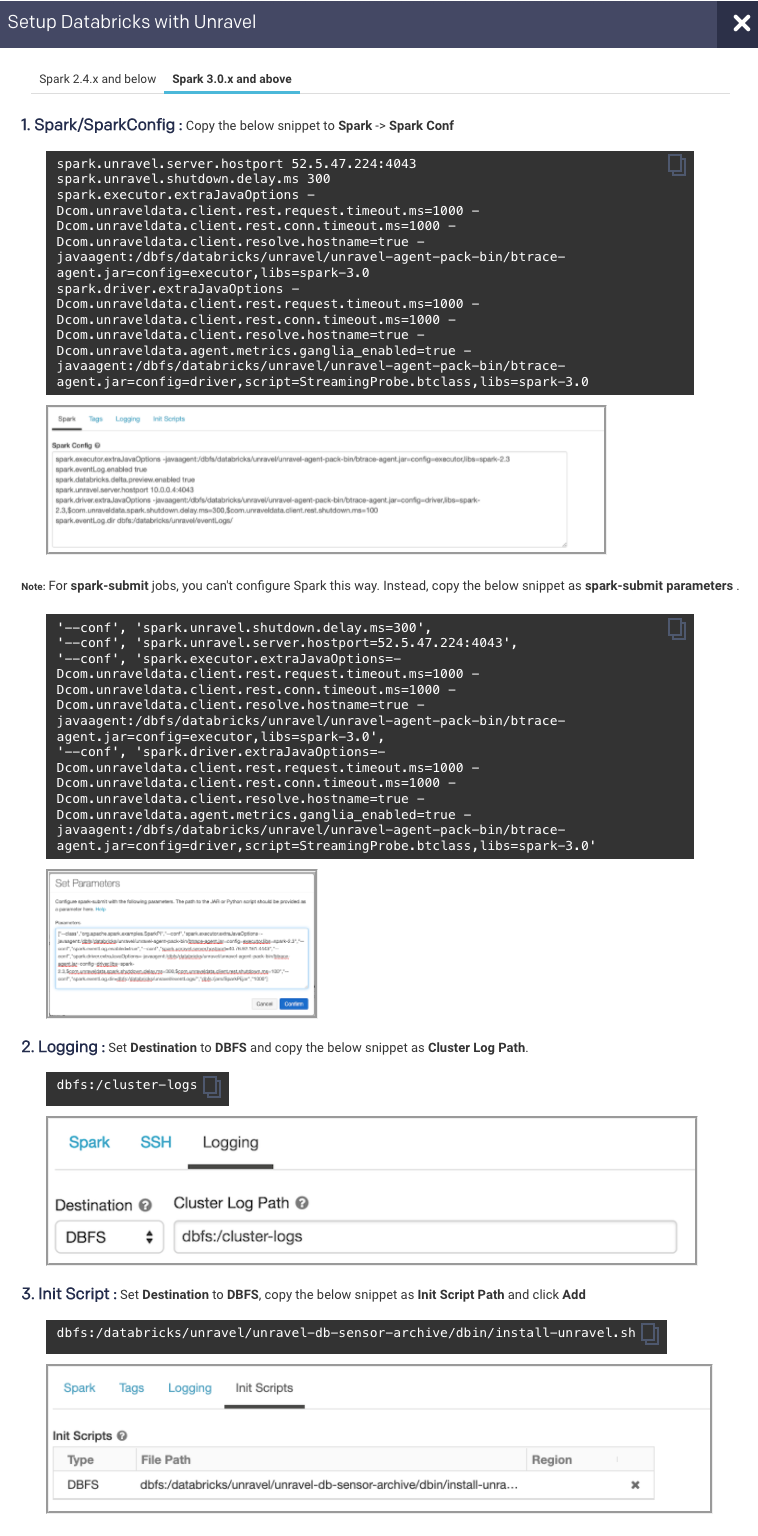
Tip
By default, the Ganglia metrics are enabled with Dcom.unraveldata.agent.metrics.ganglia_enabled property set to true.
Note
To add Unravel configurations to job clusters via API, use the JSON format as follows:
{ "settings": { "new_cluster": { "spark_conf": { // Note: If extraJavaOptions is already in use, prepend the Unravel values. Also, for Databricks Runtime with spark 2.x.x, replace "spark-3.0" with "spark-2.4" "spark.executor.extraJavaOptions": "-Dcom.unraveldata.client.rest.request.timeout.ms=1000 -Dcom.unraveldata.client.rest.conn.timeout.ms=1000 -Dcom.unraveldata.client.resolve.hostname=true -javaagent:/dbfs/databricks/unravel/unravel-agent-pack-bin/btrace-agent.jar=config=executor,libs=spark-3.0", "spark.driver.extraJavaOptions": "-Dcom.unraveldata.client.rest.request.timeout.ms=1000 -Dcom.unraveldata.client.rest.conn.timeout.ms=1000 -Dcom.unraveldata.client.resolve.hostname=true -Dcom.unraveldata.agent.metrics.ganglia_enabled=true -javaagent:/dbfs/databricks/unravel/unravel-agent-pack-bin/btrace-agent.jar=config=driver,script=StreamingProbe.btclass,libs=spark-3.0", "spark.unravel.server.hostport": "127.0.0.1:4043", "spark.unravel.shutdown.delay.ms": "300", // rest of your spark properties here ... ... }, "init_scripts": [ { "dbfs": { "destination": "dbfs:/databricks/unravel/unravel-db-sensor-archive/dbin/install-unravel.sh" } }, // rest of your init scripts here ... ... ], "cluster_log_conf": { "dbfs": { "destination": "dbfs:/cluster-logs" } }, // rest of your cluster properties here ... ... }, ... } }Set additional configurations if required.
Configure the Workspace for Data page.
Optionally, you can run healthcheck, at this point, to verify that all the configurations and services are running successfully.
<unravel_installation_directory>/unravel/manager healthcheck
Healthcheck is run automatically on an hourly basis in the backend. You can set the healthcheck intervals and email alerts to receive the healthcheck reports.
Tip
The workspace setup can be done at any time and does not impact the running clusters or jobs.
Run the following from a DBFS command-line interface:
-bash-4.2$ dbfs cat dbfs:/databricks/unravel/unravel-db-sensor-archive/etc/unravel_db.properties
Following is a sample of the output:
#Thu Sep 30 20:06:42 UTC 2021 unravel-server=01.0.0.1\:4043 databricks-instance=https\://adb-0000000000000.18.adatabricks.net databricks-workspace-name=DBW-xxx-yyy databricks-workspace-id=0000000000000 ssl_enabled=False insecure_ssl=True debug=False sleep-sec=30 databricks-token=xxxx00xx0xx00x0000x00x0000xxxx00x-
Note
You must ensure to set the property unravel-server to an FQHN or IP which can be reached by the VM in the workspace. If VNET peering is not used, private IP or FQHN is not valid. In such a case, you must use a public IP/FQHN instead.