Installing Unravel Server on a GCE VM
This topic explains how to create a new GCE instance, install and configure Unravel Server on the new GCE instance, and connect it to the GCE cluster you want to monitor.
Important
If you have not already done so, confirm your cluster meets Unravel's hosting requirements.
1. Create a GCE instance
On your GCP console, go to the GCEs dashboard and click Create Instance.
Select the following options based on Unravel's instance requirements:
Base OS
Instance type and size
GCE instance's Firewall Rules / IAM role
Best practice is to create an IAM role that contains the policy that only reads the specific Cloud storage bucket used on Dataproc cluster. Then create an instance profile and add the IAM role to it.
Ports
Networking
The GCE instance must be in the same region with the target Dataproc clusters which the Unravel compute node is monitoring.
Firewall rules or policies
Create a Cloud storage ReadAccess only IAM role and assign it to Unravel GCE to read the archive logs on the Cloud storage bucket configured for the Dataproc cluster.
Create TCP and UDP connections from the Dataproc master node to Unravel Compute node.
Create a firewall rule that allows port 3000 and port 4043 from Dataproc cluster nodes' IP address, and put the member of the Firewall Rules used on Dataproc cluster in this rule.
Sample inbound rule Type
Protocol
Port range
Source
All traffic
All
All
For example, 10.10.0.0/16
SSH
TCP
22
0.0.0.0/0 or trusted public IP for SSH access
Custom TCP Rule
TCP
3000
Custom TCP Rule
TCP
4043
Sample outbound rule Type
Protocol
Port range
Source
All traffic
All
All
0.0.0.0/0
Note
The GCE instance should have all TCP access to the Dataproc cluster (server/parent or worker) nodes. You can grant access by inserting adding firewall rules of the Dataproc server/parent and worker with all TCP, all port range.
If it isn't possible to allow the Unravel VM access to all traffic to Dataproc cluster, you must minimally allow it to access cluster nodes' TCP ports 9870, 9866 and 9867.
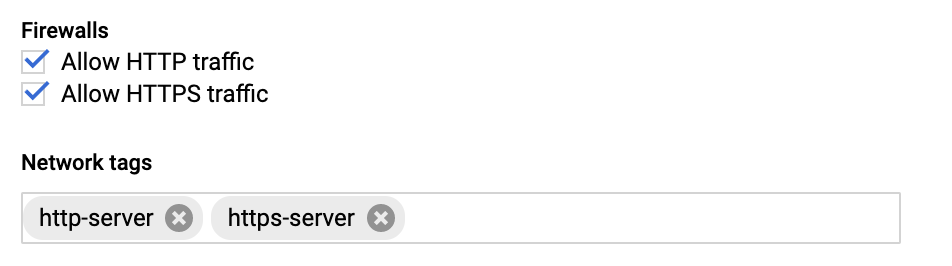
While creating the GCE instance add the Firewall properties, Enable the HTTP and HTTPS traffic Go to Network tab and add Network tags. (This is the firewall rules that is already created.)
2. Configure the GCE instance
Disable
selinux.sudo setenforce Permissive
Edit
/etc/selinux/configto make sure the setting persists after reboot and make sureSELINUX=permissive.sudo vi /etc/selinux/config
Install
libaio.x86_64,lzop.x86_64, andntp.x86_64.sudo yum install -y libaio.x86_64 sudo yum install -y lzop.x86_64 sudo yum install -y ntp.x86_64
Start ntpd and check the system time.
sudo service ntpd start sudo ntpq -p
Create a new user named
hadoop.sudo useradd hadoop
4. Install the Unravel RPM on the GCE instance
Download the Unravel Server RPM.
Install the Unravel Server RPM.
The precise filename can vary, depending on how it was fetched or copied.
sudo rpm -U unravel-4.5.0.*-EMR-latest.rpm
Switch User and User-group to
hadoophadoop.sudo /usr/local/unravel/install_bin/switch_to_user.sh hadoop hadoop
Add the following property to
/usr/local/unravel/etc/unravel.properties:com.unraveldata.onprem=false
For monitoring Dataproc Spark service, add the following properties to
/usr/local/unravel/etc/unravel.properties:com.unraveldata.spark.live.pipeline.enabled=true com.unraveldata.spark.hadoopFsMulti.useFilteredFiles=true com.unraveldata.spark.events.enableCaching=true
The installation creates the following items:
Virtualization type: HVM
User
unravel(if it doesn't exist already)./etc/init.d/unravel_*scripts for controlling services, and/etc/init.d/unravel_all.shwhich you can use to manually stop, start, and get status of all daemons in proper order.
6. Log into Unravel UI
Start Unravel daemons.
sudo /etc/init.d/unravel_all.sh start
Create an SSH tunnel from your workstation to the Unravel GCE instance.
ssh -i ssh_key.pem centos@
unravel-host-ip-L 3000:127.0.0.1:3000Using a supported web browser (see Unravel's Google Dataproc compatibility matrix), navigate to
http://127.0.0.1:3000and log in with usernameadminwith passwordunraveldata.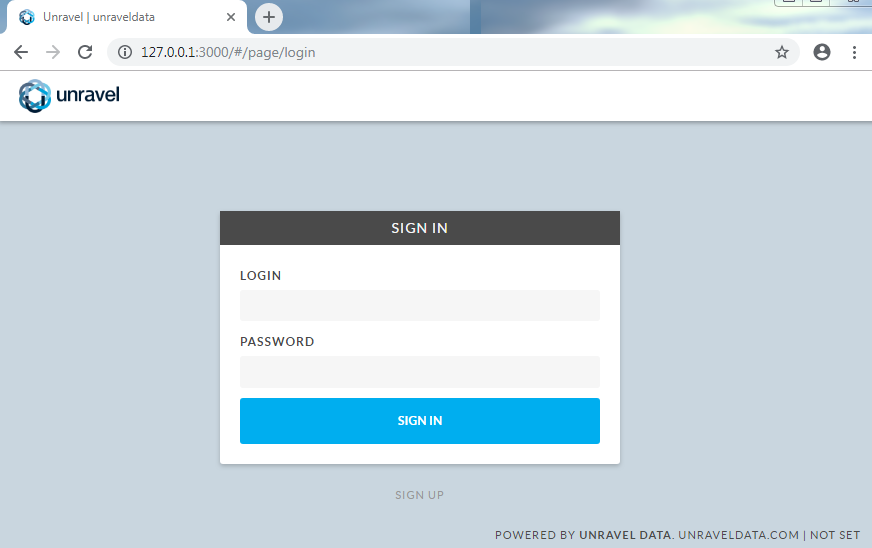
See Unravel product documentation to learn how to use Unravel.